NEAR Protocol Overview
Overview:
The NEAR Protocol, often known as NEAR, is a decentralized application (DApps) platform that is intended to support and power the open web of the future.
The CMP of NEAR on 31st December is $15.38
What is DApps?
Decentralized applications, commonly referred to as “dApps” or “dapps,” are computer programs that operate on a blockchain network of computers rather than on a single computer. The protection of user privacy, the lack of censorship, and the development freedom are all advantages of dApps. Prime examples of DApps would be Decentraland, Uniswap, OriginTrail, and IDEX.
What is Near Protocol?
NEAR Protocol is a piece of software designed to encourage a network of computers to run a platform that allows developers to construct and deploy decentralized apps. The notion of sharding, which tries to break the network’s architecture into many pieces so that computers, also known as nodes, only have to handle a portion of the network’s transactions, is central to the NEAR Protocol’s design.

Why Near Protocol matters and its problem-solving capabilities
None of the initial blockchain networks, nor those that came after them, have been able to bridge the gap between general adoption of the apps developed on top of them and the size required to sustain a whole Web.
The technological architecture of early blockchain platforms causes significant issues with usability and scalability, both of which are critical for widespread acceptance. To solve these issues in present living networks, entire living ecosystems would have to undergo major and intricate alterations.
The NEAR platform and structure were created specifically to address the issues of usability and scalability. The Network’s organization and governance structure were built to ship quickly and adapt regularly, ensuring that it always has a competitive advantage.
The most basic piece of infrastructure given is the core platform, which is made up of a cloud of community-operated validator nodes.
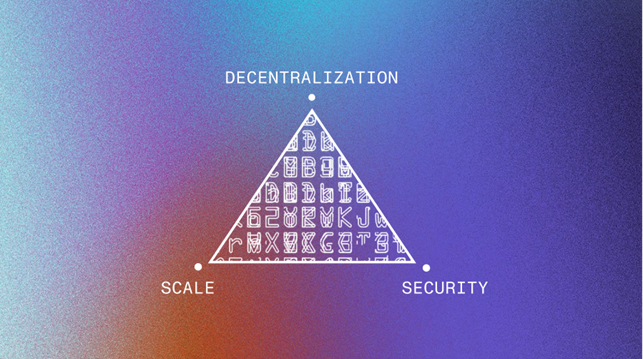
NEAR is an example of gen-3 blockchains, which attempt to tackle scalability difficulties and let both end-users and developers take advantage of smart contracts and blockchain technology to its full potential. Rather than depending on layer-2 technology, NEAR rejects the notion that every node in the network must perform all of the code, as this would create a single large inefficient bottleneck that would slow down all other techniques.
To address this problem, NEAR employs a method known as sharding, which is already widely used in the database field. It permits the network’s capacity to scale up as the number of nodes in the network grows, hence there is no theoretical limit to the network’s capacity if it is correctly implemented. What’s the best part? Sharding is a scaling approach that works at the layer 1 level
What is Sharding?
In a database, you may encounter huge, bulky data on occasion. This has a significant impact on performance and flow, as well as making the overall process inefficient. This is where the concept of sharding comes into play. Sharding divides your database horizontally and divides it into smaller, more manageable tables.
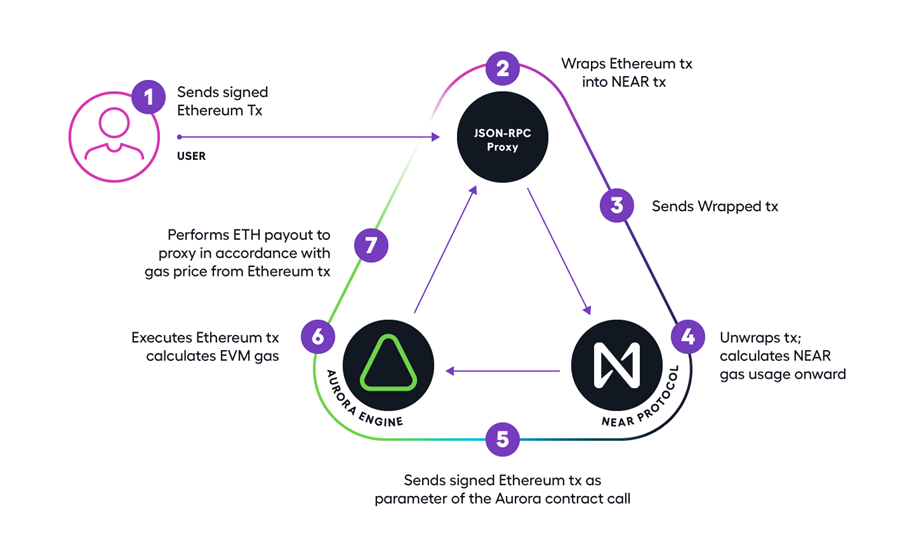
Use cases:-
- DeFi:- NEAR makes DeFi more accessible to the general public. DeFi is now live on NEAR and open for everyone and users throughout the world, thanks to the opening of the Rainbow Bridge i.e any information that is cryptographically verifiable on NEAR may be used in Ethereum contracts, and vice versa, thanks to the Rainbow Bridge. All Ethereum-based assets, which already number in the tens of billions, are now fully functional in NEAR applications.
- Non Fungible Tokens(NFTs):- NFTs are digital items that exist on the NEAR blockchain, and the artist can be notified and given a commission every time they are bought and sold. At all times and in all places. Not only that, but the NFT can be configured to split the cash indefinitely whichever you like – perhaps 10% goes to the artist, 5% to the agency that helped produce it, 4% to the artist’s union, and 1% to a charity they favor. Perhaps 5% is divided among all past owners of this NFT, incentivizing them to help it maintain its worth.
The NEAR token is the ecosystem’s primary native asset, and all accounts have access to it. Each token, identical to Ether, is a one-of-a-kind digital asset that may be used to:
- For completing transactions and keeping data, you must pay the system.
- Participate in the staking procedure to run a validating node as part of the network.
- Participating in governance procedures can help influence how network resources are distributed and where the network’s future technological direction will go.
Tokenomics
NEAR Protocol launched its mainnet on April 22, 2020, with 1 billion NEAR tokens created at genesis. 5% of additional supply is issued each year to support the network as epoch rewards, of which 90% goes to validators (4.5% total) with the total circulating supply of 60M tokens and 10% to the protocol treasury (0.5% total). 30% of transaction fees are paid out as rebates to contracts that interact with a transaction, while the remaining 70% are burned. Inflation, transfers, and vesting schedules did not begin until the final phase of NEAR’s mainnet rollout, which started on October 13, 2020. NEAR Protocol uses Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus to secure and validate transactions on the blockchain.
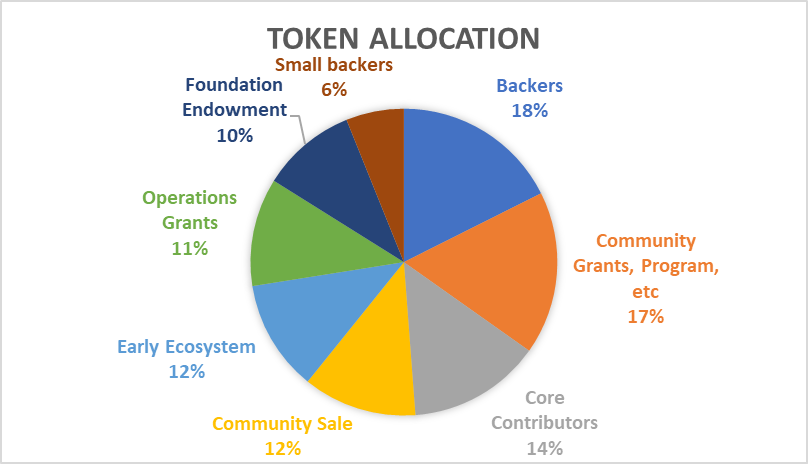
What is early blockchain ecosystem mean?
You can define a blockchain ecosystem as the agreed-upon governance structure for a specific use case. The governance structure provides a definition of the acceptable behavior of participants, data ownership, funding, exit and entrance criteria, and conditions for information sharing among participants.
What is a backer?
Backer means an investor, mortgagee, bondholder, note holder, or another source of equity, capital, or other assets, other than a financial institution
Competition Analysis
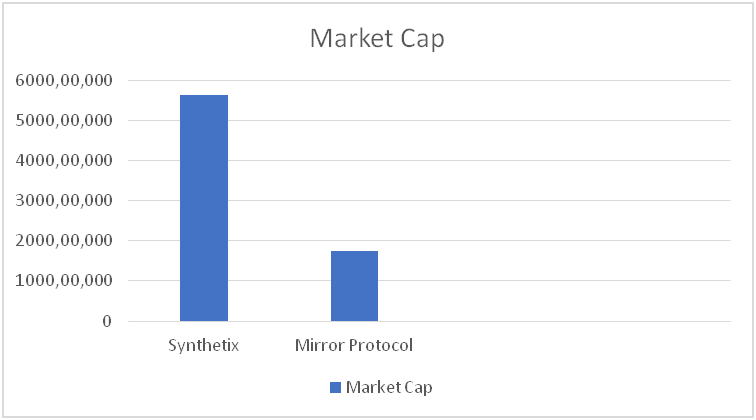
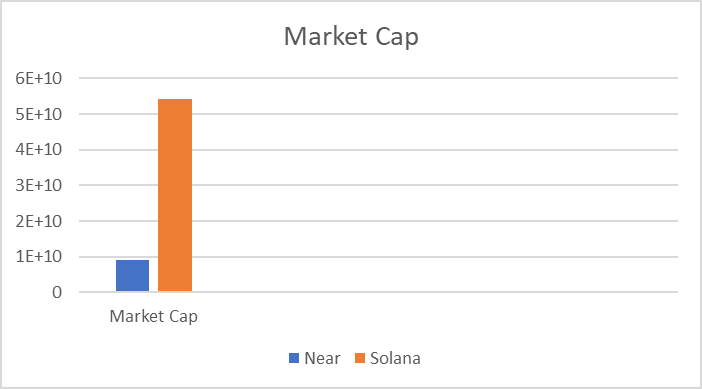
Near protocol vs Solana
Technologically, these projects are very similar and solve the same problem – the scalability of decentralized technologies on the Internet.
The projects perform almost the same function, but the Solana ecosystem is much more developed than the Near Protocol.
But in some ways, Near is ahead of Solana’s technological advancement. Offering by the user gas-free DeFi by means of Aurora and low commissions with a maximum commission throughput rate of 100k tps
Team, Media & Community strength
Alexander Skidanov, a former Microsoft employee, and Ilya Polosukhin, a developer, created NEAR Protocol. The project started in late 2018 and is still ongoing. Since then, the team has grown to fifty members, including Facebook, Google, and Niantic developers, as well as several medalists and finalists from international sports programming contests. Two members of the team have twice won the programming world championship (there are nine such people in the world). The Russian Federation and former Soviet Union countries account for nearly all of the team’s members.
Near protocol’s social media family is growing at an exponential rate. They have over 247.5K followers on Twitter and 37K in telegram in just over 3 years. They’ve been recently featured in Nasdaq on 8th December 2021. It caught an eye by this channel because of its skyrocketing performance in the first week of December. It’s been getting attention this year because of the performance it has shown in this past year.
Conclusion
It is easy to be excited about Near Protocol. The team has a solid scalability solution to current issues on Ethereum and other blockchain platforms. It also introduces features, like private shards, offering enterprises to host their chain essentially without giving up the privacy of their data. We expect great things from NEAR as it onboards more users and an ecosystem is created. It will be interesting to see whether their tech will be adopted by large enterprises. It is definitely worth keeping an eye on this blockchain.
NEAR is a groundbreaking system that is meant to successfully address the issues that existing blockchains experience. The NEAR protocol is driving the crypto and blockchain industry ahead with its broad resourcing and simplicity of use; NEAR is a shining example of how a balance of seamless development, scalability, and security can be accomplished. It has a total supply of 1B tokens with a 60% circulation supply.
Individuals interested in Ethereum alternatives or Web 3.0 are more attracted to NEAR. News of partnership with Terra earlier this week has catalyzed significant increases. Investors are digesting the news and flooding the protocol with new funds.
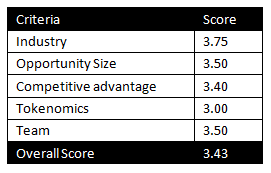
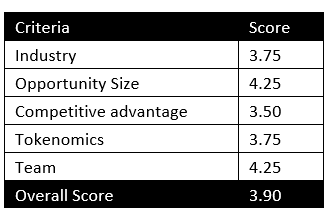
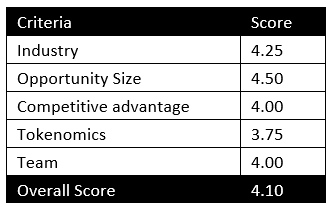
MintingM rating for Near Protocol: 3.85/5
| Criteria | Score |
| Industry | 3.75 |
| Opportunity Size | 4.25 |
| Competitive advantage | 4.00 |
| Tokenomics | 3.75 |
| Team | 3.50 |
| Overall Score | 3.85 |
Important links and sources
Get deeper insights into the crypto market’s weekly trends discussed on our Spotify podcast.
Start your Crypto Investments with XMINT Bots today